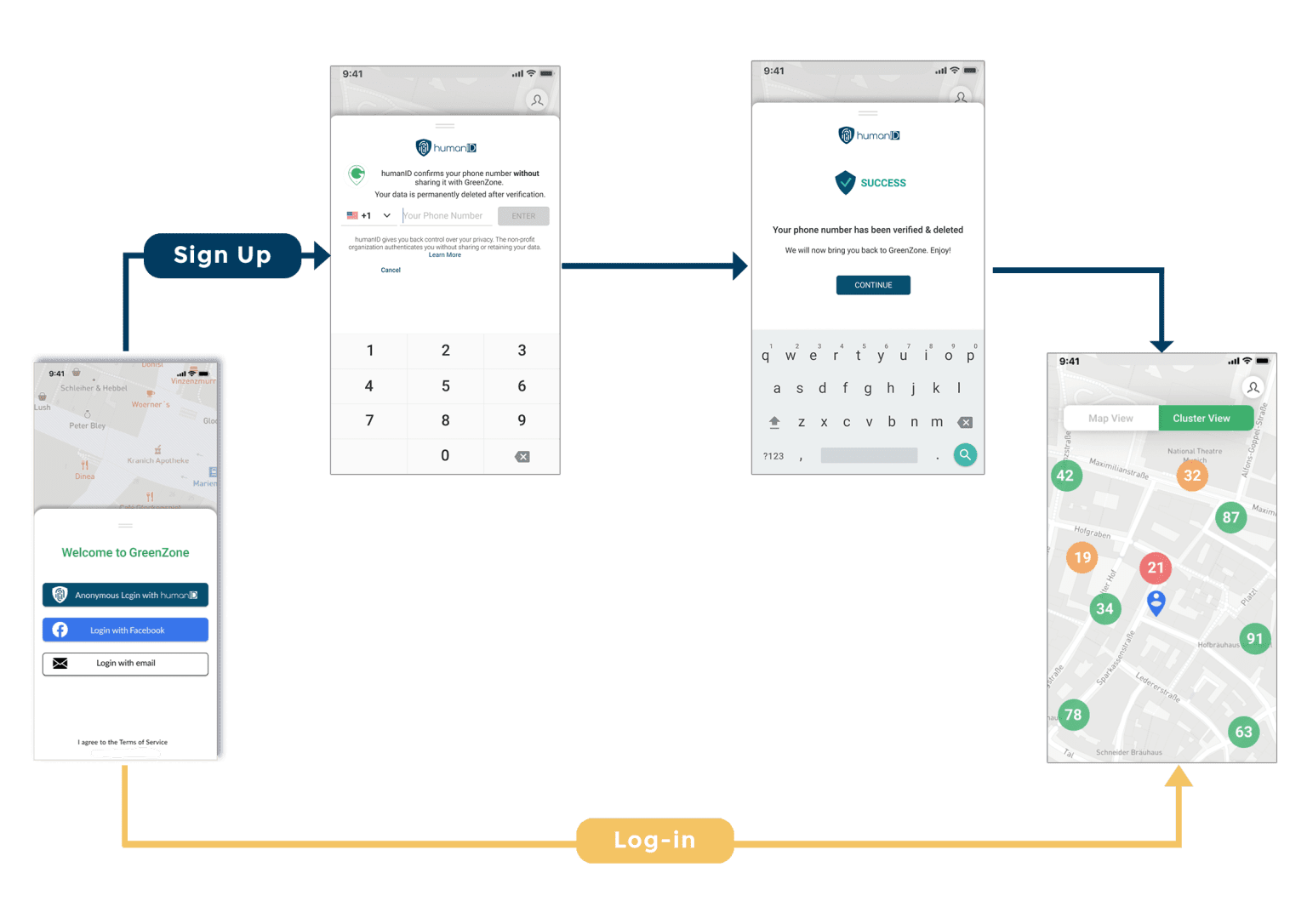
How does Single Sign-On work?
By Caroline Wang
May 7. 2021
With the rapid growth of the internet and technology comes the risks of privacy protection and cybersafety. Passwords are one of the simplest security devices the internet utilizes for user protection. However, many believe that passwords are outdated and less effective. Passwords are a hassle for users to remember and come with the inconvenience of resetting them when forgotten. Thus, many companies opt for alternative security strategies. Among these alternatives is single sign-on, which presents a simple solution to the password problem.
What is Single Sign-On?
Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication method for users to securely log into multiple applications and accounts with a single set of credentials. The purpose of using a single set of credentials alleviates the inconvenience for users when accessing multiple, related websites. SSO reduces the number of login screens a user must encounter which increases the time spent on a web application. To illustrate this, take a real-world example in a bar setting. Most bars admit customers upon checking their identification card once. But imagine if, for every alcoholic beverage purchase, customers had to show their credentials. Many would quickly become frustrated with the inconvenience and would possibly leave. To avoid this issue, these establishments usually only check a consumer’s identification once. SSO is analogous to this example because it ensures that a user only needs one set of credentials to access multiple websites and applications.
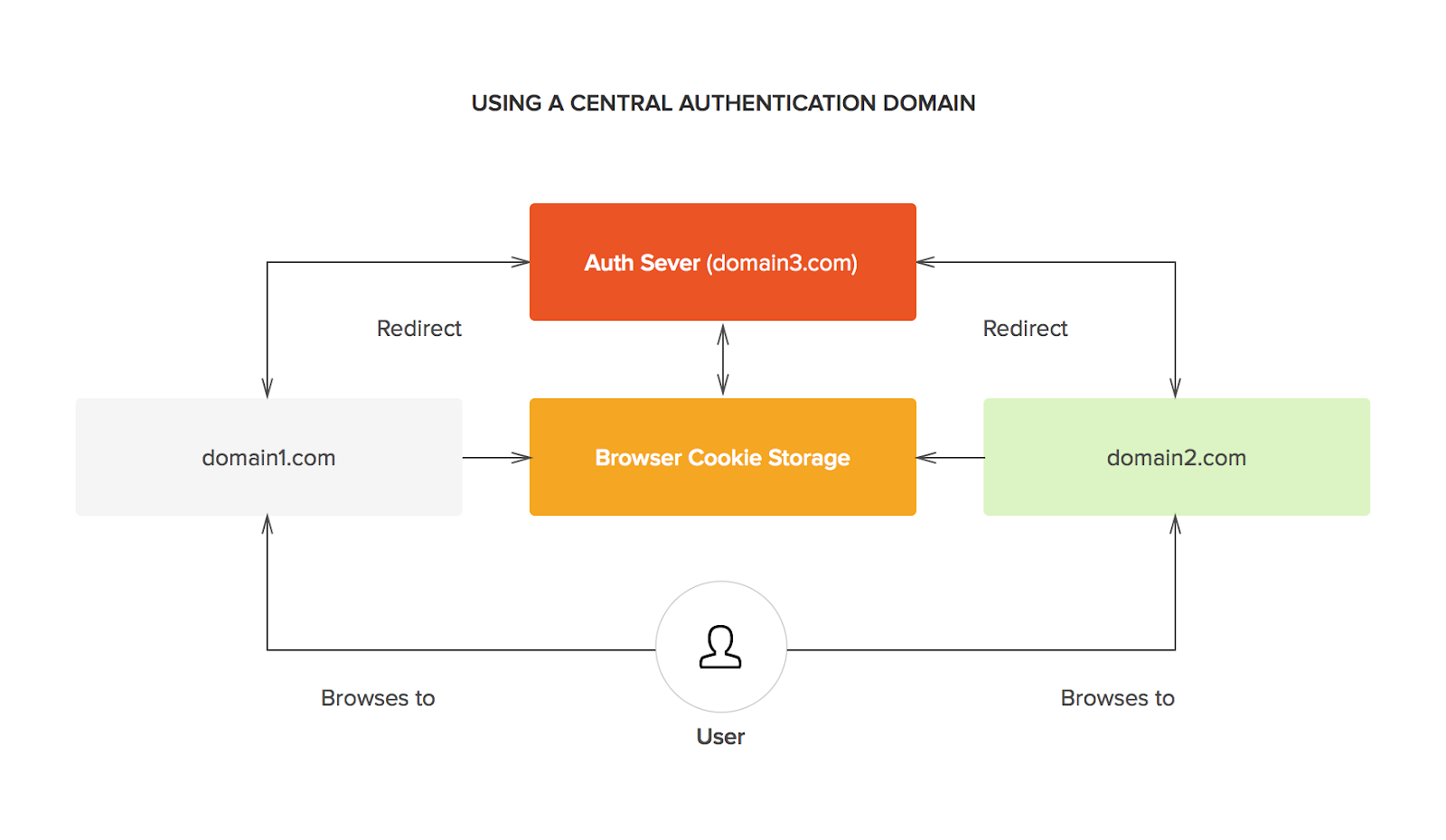
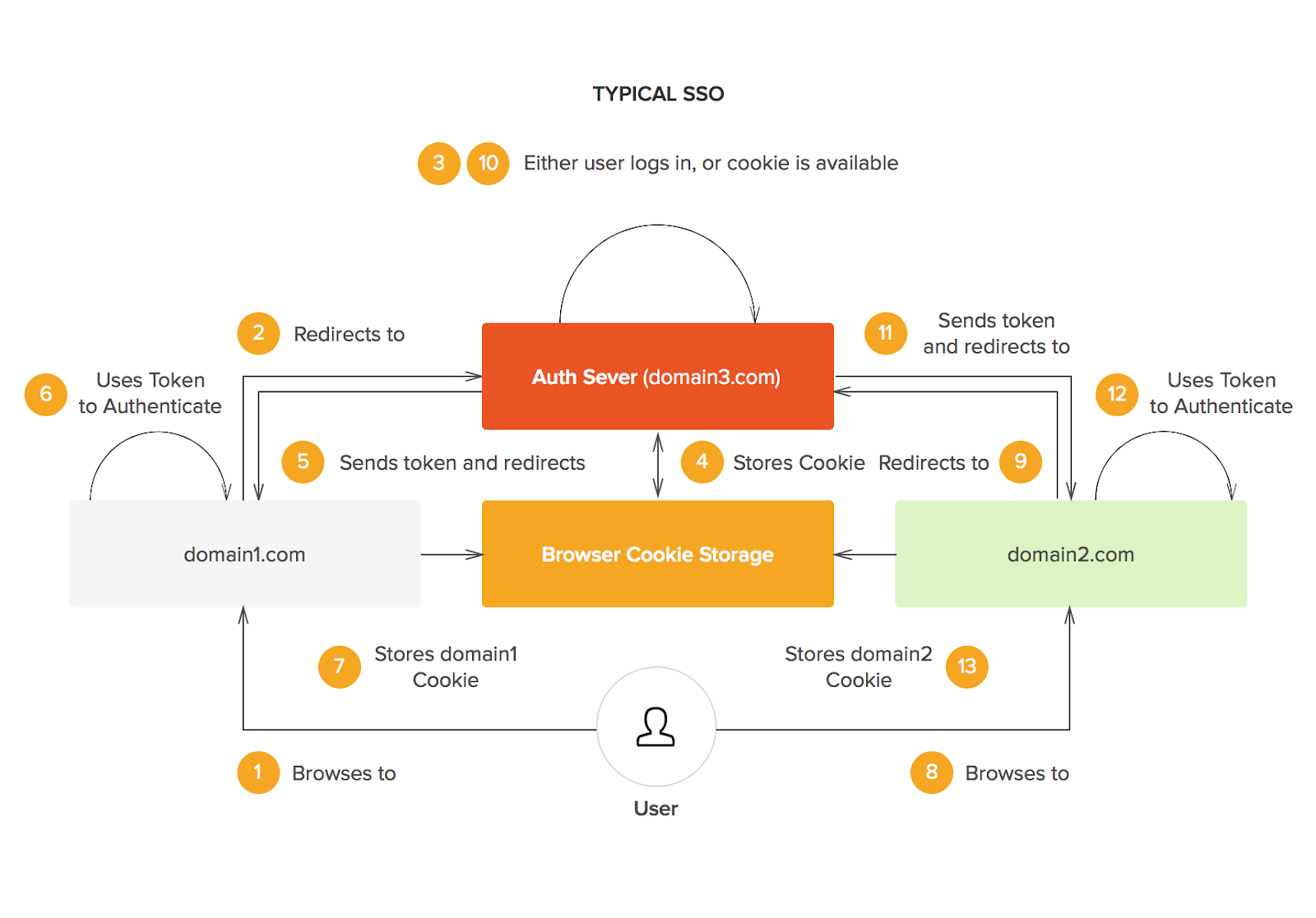
How does Single Sign-On work?
The foundation for SSO success is built upon trust between multiple parties. The service provider, or the application, and the identity provider, like humanID, must be perfectly transparent with one another in order to provide users seamless and secure access to multiple web resources. This trust is typically verified through the exchange of a certificate between both parties which can be used to identify information sent from the identity provider and service provider. In SSO, these bits of information, known as SSO tokens, are typically user credentials like email or username.
The overarching flow of SSO logins are condensed as follows:
- A user browses the application or the service provider they want to access.
- The service provider sends a token of information to the identity provider, the SSO system, to request the user’s access. This is usually something like their email address.
- The identity provider checks if the user has already been authenticated through another application. If the user has a previous login, access will be granted and the service provider will skip to step 5.
- If the user has no previous login, they will be prompted to do so by the identity provider. This would be some form of one-time password (OTP) which would be a simple username and password.
- After the identity provider authenticates the user’s credentials, it will send the token of information back to the service provider to confirm a successful verification.
- Once the token is received by the service provider, it is validated once more according to the certification between the two providers during the establishment of the partnership.
- Access to the service provider is granted for the user.
Advantages of Single Sign-On
In addition to being a more convenient and efficient login process for users, SSO is widely established to be more secure. At first glance, this may seem counterintuitive since there is only one password involved as opposed to multiple across applications. However, SSO provides multiple reasons as evidence of its increased security. For starters, the password a user creates with SSO is stronger. Since the user would only need to remember one password, they have no need to create simpler, easy-to-remember (and easy-to-guess) passwords. This also prevents a user from creating repeated passwords across applications which would provide a cybercriminal access to multiple accounts once a single one has been breached. SSO prompts users to focus their attention on a single, super-secure password which nearly eliminates the risk of being guessed from another user.
As a result of having fewer passwords altogether, a user saves time that may be wasted on password recovery. With multiple passwords comes the risk of forgetting them across applications. SSO cuts the amount of time a user might spend on recovering and resetting lost passwords by having one centralized login location. This way, a password is lost with SSO, only a single set of recovery actions must be taken rather than multiple, individual recoveries across websites.
SSO also has the advantage of being a single anchoring point across multiple websites. Thus, there is only one point for enforcing password re-entry after a user is idle for extended periods of time. Rather than having a user re-enter their passwords across multiple applications, a single point of re-entry with SSO should easily provide the user with all the websites they were previously accessing.
humanID as a Single Sign-On
humanID is a one-click, anonymous login solution that ensures a safer online experience by ensuring each user’s privacy and anonymity while preventing spam accounts and bot misinformation. By assigning each user a non-reversible, hashed identifier, humanID acts as the identity provider in the SSO relationship. However, humanID differs from other SSO options by providing complete anonymity for each user who signs in. humanID immediately deletes a user’s data upon authentication and never shares such information with any third parties. By using a user’s phone number as the irreversible, hashed identifier, humanID can verify any user’s login credentials from numerous applications and can prevent the creation of a spam account. More specifically, humanID has two levels of hashing to provide the highest level of privacy protection. First, a user’s phone number is hashed and salted, then immediately deleted. Following this first hash, the salted hash is stored as the username for the specific application’s login. Because each user has distinct hashes for each application they sign up for, humanID safeguards their information while allowing users to log into multiple platforms. Therefore, humanID provides the added advantage of entirely eliminating the need for passwords with its technology. With humanID’s technology, users are guaranteed a convenient and secure login experience.